1. 基于大语言模型的 AI Agents
1.1. 什么是 AI Agent?
代理(Agent)强调自主性和主动性。 智能代理/智能体是以智能方式行事的代理; Agent 感知环境,自主采取行动以实现目标,并可以通过学习或获取知识来提高其性能。
一个精简的 Agent 决策流程:
- 感知(Perception):是指 Agent 从环境中收集信息并从中提取相关知识的能力。
- 规划(Planning):是指 Agent 为了某一目标而做出的决策过程。
- 行动(Action):是指基于环境和规划做出的动作。 其中,Policy是 Agent 做出 Action 的核心决策,而行动又通过观察(Observation)成为进一步 Perception 的前提和基础,形成自主地闭环学习过程。
1.2. 背景知识
做决策的过程中,一个很重要的信息来源是记忆。 下面简单介绍下都有哪些种类的记忆。
1.2.1. 记忆
| 记忆类型 | 映射 | 例子 |
|---|---|---|
| 感觉记忆 | 学习原始输入的嵌入表示,包括文本、图像等,短暂保留感觉印象。 | |
| 短期记忆 | 上下文学习(比如直接写入 prompt 中的信息),处理复杂任务的临时存储空间,受 Transformer 有限的上下文窗口。 | |
| 长期记忆 | 在查询时智能 Agent 可以关注的外部向量存储,具有快速检索和基本无限的存储容量。 |
1.2.2. 怎么写好 Prompt:ReAct
ReAct指:Reason and Act。
特色:
- CoT 只是在 prompt 中加入静态的“Lets think step by step”。ReAct 的 Prompt 是动态变化的。
- CoT 只调用 LLM 一次,ReAct 是多次迭代调用 LLM。
ReAct可能是当前 Agent 中使用最多的 prompt 结构:少样本+Thought, Action,Observation。也就是调用工具、推理和规划时常用的 prompt 结构。
ReAct迭代使用Thought、Action、Observation。 其中Thought、Action由 LLM 生成,Observation 是执行 Action 后获得的结果。
- Step1:基于 Question 先 think(reasoning),再决定采取什么行动。这样 LLM 就会生成 Thought 1 和 Action 1 。执行 Action 1 获得 Observation 1。
- Step2:基于 Question,Thought 1 ,Action 1 和 Observation 1,汇总所有信息先 think,再决定采取什么行动。LLM 就会生成 Thought 2 和 Action 2。执行 Action 2 获得 Observation 2。
- 以此类推直到 Action 表示结束。
1.3. 例子:来自斯坦福的虚拟小镇
Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior Github Code
虚拟小镇,一个 agent 就是一个虚拟人物,25 个 agents 之间的故事。
1.3.1. 架构
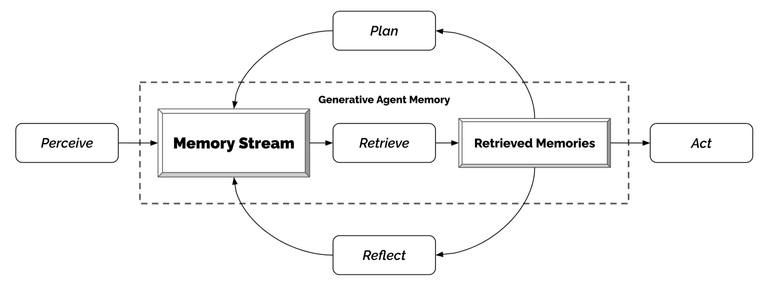
1. 记忆流与检索
记忆流(Memory Stream)记录了代理(Agent)的所有经历。 它是一个内存对象列表,其中每个对象包含自然语言描述,创建时间戳和最近访问时间戳。 记忆流的最基本元素是观察,这是代理直接感知的事件。 常见的观察包括代理自己执行的行为,或者代理感知到的其他代理或非代理对象执行的行为(每个Agent都有自己独立的记忆流)。
检索功能以代理的当前情况作为输入,检索出一部分记忆流,以传递给语言模型。 排序打分包括三个部分:
- 近期性(Recency):为最近访问的记忆对象分配更高的分数,因此刚刚发生的事件或今天早上的事件可能会保留在代理的注意力范围内。在作者的实现中,将近期性视为一个指数衰减函数,衰减的对象是自上次检索记忆以来的沙盒游戏小时数。衰减因子是0.99。
重要性:通过为代理认为重要的记忆对象分配更高的分数,区分了平凡记忆和核心记忆。
Prompt:
On the scale of 1 to 10, where 1 is purely mundane (e.g., brushing teeth, making bed) and 10 is extremely poignant (e.g., a break up, college acceptance), rate the likely poignancy of the following piece of memory. Memory: buying groceries at The Willows Market and Pharmacy Rating: <fill in>
- 相关性:为与当前情况相关的记忆对象分配更高的分数。使用常见的向量检索引擎即可。
最终的检索分数是上面三项的加权平均。
2. 反思(Reflection)
挑战:仅配备原始观察记忆的代理,往往难以进行概括或推理。
示例:用户问 Klaus Mueller:“If you had to choose one person of those you know to spend an hour with, who would it be?” 仅通过观察记忆,代理简单地选择 Klaus 交互最频繁的人:Wolfgang,他的大学宿舍邻居。 但是,Wolfgang 和 Klaus 只是偶尔见面,没有深入的互动。 一个更理想的回答需要代理从 Klaus 花费数小时在研究项目上的记忆中概括出 Klaus 对研究的热情,并同样认识到 Maria 也在她自己的研究中付出努力(尽管是在不同的领域),从而反映出他们有共同的兴趣。 使用下面的方法,当问 Klaus 要与谁共度时间时,Klaus 会选择 Maria 而不是 Wolfgang。
作者引入了第二种类型的记忆,称之为反思。 反思是由代理生成的更高级别、更抽象的思考。 因为反思也是一种记忆,所以在检索时,它们会与其他观察结果一起被包含在内。 反思是周期性生成的;在作者的实现中,当代理感知到的最新事件的重要性评分之和超过一定阈值时,就会生成反思。 在实践中,代理大约每天反思两到三次(一日三省吾身)。
反思的第一步是让代理确定要反思什么,通过确定代理最近的经历可以提出哪些问题。 作者用代理记忆流中最近的100条记录查询 LLM, 使用 Prompt:“Given only the information above, what are 3 most salient high-level questions we can answer about the subjects in the statements?”, 生成候选问题。
第二步,将这些生成的问题作为检索的查询,收集每个问题的相关记忆(包括其他反思)。 然后使用 LLM 从中抽取洞见(insight),并引用生成洞见对应的特定记录。 洞见将被解析,且存储为记忆流中的一个反思,包括指向被引用的内存对象的指针。
反思(Reflection)明确允许代理不仅反思他们的观察结果,还可以反思其他的反思。 因此,代理生成了反思树:树的叶节点代表基础观察,非叶节点代表的思考越往树上越抽象和高级。
3. 计划与响应
计划(Plan) 是为了做更长时间的规划。
像反思一样,计划也被储存在记忆流中(第三种记忆),并被包含在检索过程中。 这使得代理能够在决定如何行动时,同时考虑观察、反思和计划。 如果需要,代理可能在中途改变他们的计划(即响应,reacting)。
为了创建这样的计划,作者的方法是从上到下,递归地生成更多的细节。 第一步是创建一个大致概述一天行程的计划。 为了创建初始计划,使用代理的摘要描述(例如,名字,特征,和他们最近经历的总结)和他们前一天的总结来提示语言模型。 下面是一个完整的示例提示,底部未完成,由 LLM 完成:
Name: Eddy Lin (age: 19)
Innate traits: friendly, outgoing, hospitable Eddy Lin is a student at Oak Hill College studying music theory and composition. He loves to explore different musical styles and is always looking for ways to expand his knowledge. Eddy Lin is working on a composition project for his college class. He is also taking classes to learn more about music theory. Eddy Lin is excited about the new composition he is working on but he wants to dedicate more hours in the day to work on it in the coming days.
On Tuesday February 12, Eddy 1) woke up and completed the morning routine at 7:00 am, [. . . ] 6) got ready to sleep around 10 pm.
Today is Wednesday February 13. Here is Eddy's plan today in broad strokes: 1)
代理将此计划保存在记忆流中,然后递归分解它以创建更细粒度的动作,首先是一小时长的动作块。 然后我们再次递归分解这个计划,变成 5-15 分钟的动作块。 这个过程可以根据需要的粒度进行调整。
3.1 响应和更新计划(Reacting and Updating Plans)
代理执行动作循环中的动作,每个时间步骤,它们感知周围的世界,这些感知到的观察结果被存储在它们的记忆流中。
这些观察结果输入到 LLM,让 LLM 决定代理是否应该继续他们现有的计划,或者做出响应(reacting)。
下面是 prompt,其中[Agent's Summary Description]代表了一个动态生成的、长达一段落的对代理总体目标和性情的总结:
[Agent's Summary Description]
It is February 13, 2023, 4:56 pm.
John Lin's status: John is back home early from work.
Observation: John saw Eddy taking a short walk around his workplace.
Summary of relevant context from John's memory: Eddy Lin is John’s Lin’s son. Eddy Lin has been working on a music composition for his class. Eddy Lin likes to walk around the garden when he is thinking about or listening to music.
Should John react to the observation, and if so, what would be an appropriate reaction?
通过两个 prompts “What is [observer]'s relationship with the [obsserved entity]?” 和 “[Observed entity] is [action status of the observed entity]” 来生成上下文摘要,并将它们的答案一起总结。 输出建议 “John could consider asking Eddy about his music composition project”。 然后,从响应发生的时间开始,重新生成代理的现有计划。 最后,如果行动指示了代理之间需要互动,使用以下方式生成他们的对话。
3.2 对话
代理在互动时进行对话。根据它们对彼此的记忆来生成代理的对话。 例如,当 John 开始和 Eddy 对话时,通过使用他对 Eddy 的总结记忆以及他决定询问 Eddy 关于他的“composition project”时的预期响应来生成 John 的第一句话。
[Agent's Summary Description]
It is February 13, 2023, 4:56 pm.
John Lin's status: John is back home early from work.
Observation:John saw Eddy taking a short walk around his workplace.
Summary of relevant context from John’s memory: Eddy Lin is John’s Lin’s son. Eddy Lin has been working on a music composition for his class. Eddy Lin likes to walk around the garden when he is thinking about or listening to music.
John is asking Eddy about his music composition project. What would he say to Eddy?
从 Eddy 的角度看,John 发起的对话被视为一个他可能想要回应的事件。 因此,就像 John 做的那样,Eddy检索并总结了他与John的关系记忆,以及可能与 John 在对话中的最后一句话相关的记忆。 如果他决定回应,我们会使用他的总结记忆和当前的对话历史来生成 Eddy 的话语:
[Agent's Summary Description]
It is February 13, 2023, 4:56 pm.
Eddy Lin’s status: Eddy is taking a short walk around his workplace.
Observation: John is initiating a conversation with Eddy.
Summary of relevant context from Eddy’s memory: Jonn Lin is Eddy Lin’s father. John Lin is caring and is interested to learn more about Eddy Lin’s school work. John Lin knows that Eddy Lin is working on a music composition.
Here is the dialogue history:
John: Hey Eddy, how’s the music composition project for your class coming along?
How would Eddy respond to John?
这个对话的延续是使用同样的机制生成的,直到两个代理中的一个决定结束对话。
References